Gotten for cloud evaluation project
Gotten for cloud simulators running example
The goal here is to test cloud simulators that reproduce the behavior of data centres upon certain workload. Then, the input of these simulators are models of data centres along with models of workloads.
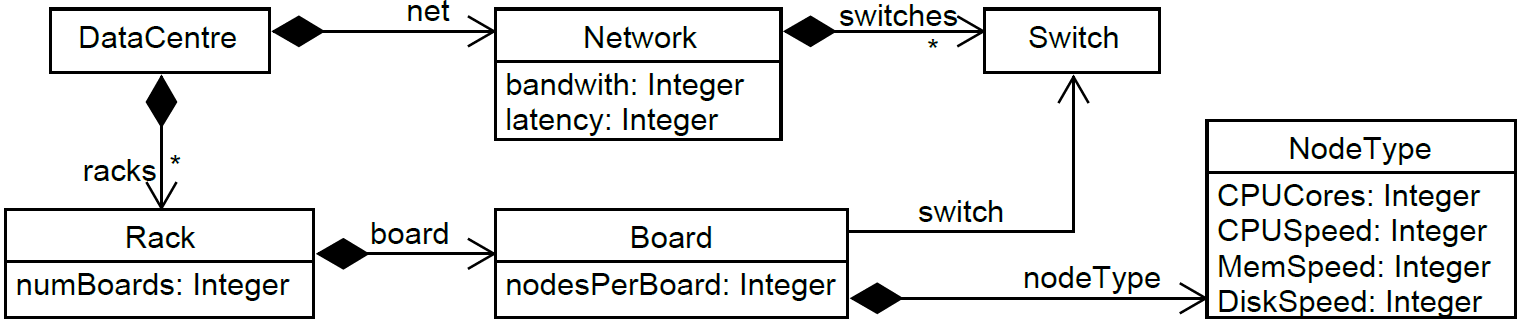
The following figure shows a meta-model to represent data centres, where a DataCentre is made of Network and any number of Racks, and each Rack contains several Boards. Boards are connected via Switches and have computing nodes with characteristics described by NodeTypes:
The mrDSL program for data centres
Since it is difficult to establish an oracle to test if a data centre simulator S performs as expected, we use MT. The following listing shows the mrDSL program created with the Gotten framework to apply MT to this data centre simulators domain:
metamodel datacentre "/sample.gotten/model/datac.ecore" with m1, m2
models "/sample.gotten/model/dcmodels"
metamodel workload "/sample.gotten/model/workload.ecore" with w1, w2
models "/sample.gotten/model/workloads"
datacentre input Features {
context DataCentre def: NNodes: Int = racks->collect(numBoards*board.nodesPerBoard)->sum()
context DataCentre def: CPU: Int = racks->collect(numBoards*board.nodesPerBoard*board.nodeType.CPUCores*board.nodeType.CPUSpeed)->sum()
context DataCentre def: NMachines: Int = racks->collect(numBoards*board.nodesPerBoard*board.nodeType.CPUCores)->sum()
context DataCentre def: Storage: Int = racks->collect(numBoards*board.nodesPerBoard*board.nodeType.DiskSpeed)->sum()
context DataCentre def: Network: Int = net->collect(bandwidth)->sum()
context DataCentre def: Memory: Int = racks->collect(numBoards*board.nodesPerBoard*board.nodeType.MEMSpeed)->sum()
}
workload input Features {
context WorkloadSet def: Workload: Set = workloads->collect(Traces)
}
output Features {
Time : Long
Energy : Long
}
Processor {
Name: String
Version: String
}
MetamorphicRelations {
MR1 = [(( CPU(m1) > CPU(m2) ) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) implies ((Energy(m1) <= Energy(m2)))]
MR2 = [(( NMachines(m1) > NMachines(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) implies ((NMachines(m1)/NMachines(m2)) >= (Energy(m1)/Energy(m2)))]
MR3 = [(( Storage(m1) > Storage(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) implies (Time(m1) <= Time(m2))]
MR4 = [(( Network(m1) > Network(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) implies (Time(m1) <= Time(m2))]
MR5 = [(( Memory(m1) > Memory(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) implies (Time(m1) < Time(m2))]
MR6 = [( ((m1) == (m2)) and ( Workload(w1)->includes(Workload(w2))) ) implies (Time(m2) <= Time(m1))]
}
MRs for data centres brief description
Below we provide a brief description of these 6 MRs for cloud simulators:
| Relation | Description |
|---|---|
| MR1 | The cloud m1 has a better CPU than m2. The workloads w1 and w2 are equal. |
| MR1i = [( CPU(m1) > CPU(m2) ) and ((w1) == (w2)) ] | |
| The energy required to execute w1 over m1 should be less than or equal to the energy required to execute w2 over m2. | |
| MR1o = [ (Energy(m1) <= Energy(m2))] | |
| MR2 | The cloud m1 contains more physical machines than the cloud m2. The workloads w1 and w2 are equal. |
| MR2i = [( NMachines(m1) > NMachines(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ] | |
| The ratio between the number of machines of m1 and m2 should be greater than or equal to the ratio between the energy consumption required to execute w1 over m1 and the one required to execute w2 over m2. | |
| MR2o = [ (NMachines(m1)/NMachines(m2)) >= (Energy(m1)/Energy(m2))] | |
| MR3 | The cloud m1 has a better storage system than m2. The workloads w1 and w2 are equal. |
| MR3i = [( Storage(m1) > Storage(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ] | |
| The time required to execute w1 over m1 should be less than or equal to the time required to execute w2 over m2. | |
| MR3o = [ (Time(m1) <= Time(m2)) ] | |
| MR4 | The cloud m1 has a better network system than m2. The workloads w1 and w2 are equal. |
| MR4i = [( Network(m1) > Network(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ] | |
| The time required to execute w1 over m1 should be less than or equal to the time required to execute w2 over m2. | |
| MR4o = [ (Time(m1) <= Time(m2)) ] | |
| MR5 | The cloud m1 has a better memory system than m2. The workloads w1 and w2 are equal. |
| MR5i = [( Memory(m1) > Memory(m2)) and ((w1) == (w2)) ) | |
| The time required to execute w1 over m1 should be less than or equal to the time required to execute w2 over m2. | |
| MR5o = [ (Time(m1) <= Time(m2)) ] | |
| MR6 | The clouds m1 and m2 are equal. The workload w1 contains w2. |
| MR6i = [ ((m1) == (m2)) and ( Workload(w1)->includes(Workload(w2))) ] | |
| The time required to execute w2 overr m2 should be less than or equal to the time required to execute w1 over m1. | |
| MR6o = [ (Time(m2) <= Time(m1)) ] |
Gotten for cloud projects download links
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science (RTI2018-095255-B-I00, project “MASSIVE”) and the R&D programme of Madrid (P2018/TCS-4314, project “FORTE”).